Embarking on an exploration of the Marshall Plan worksheet answers, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this pivotal foreign aid program. The Marshall Plan, a cornerstone of post-World War II reconstruction, stands as a testament to international cooperation and its profound impact on shaping the modern world.
Unveiling the historical context, economic ramifications, and lasting legacy of the Marshall Plan, this discourse provides a comprehensive understanding of its multifaceted nature. Through meticulous analysis and insightful commentary, we unravel the complexities of this transformative initiative, shedding light on its enduring significance.
Marshall Plan Overview

The Marshall Plan, officially known as the European Recovery Program, was a U.S.-sponsored program of economic recovery for Western Europe following the devastation of World War II. The plan was proposed by U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall in a speech at Harvard University on June 5, 1947.
The Marshall Plan aimed to provide economic assistance to help Europe rebuild its infrastructure, industry, and economy. The plan was designed to prevent the spread of communism in Europe and to promote economic stability and prosperity.
Countries that Received Aid
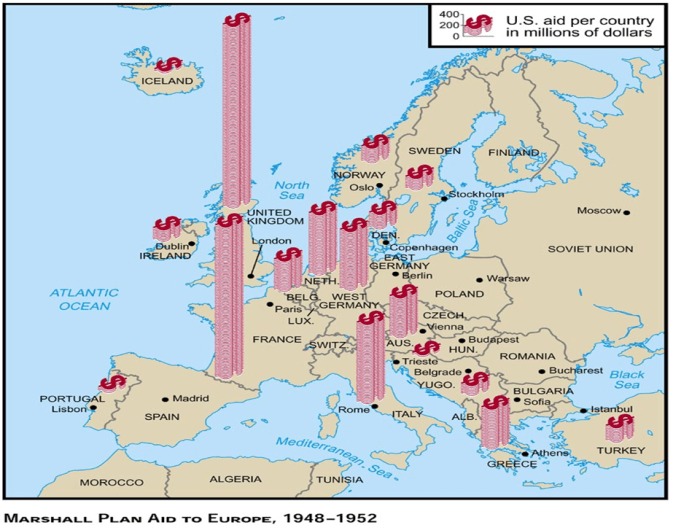
The Marshall Plan provided economic assistance to 16 Western European countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.
Amounts Provided
The Marshall Plan provided a total of $13 billion in economic assistance to Europe over a four-year period. The funds were used to purchase food, fuel, machinery, and other goods and services.
Timeline of Key Events, The marshall plan worksheet answers
- June 5, 1947:U.S. Secretary of State George Marshall proposes the Marshall Plan in a speech at Harvard University.
- April 3, 1948:The Economic Cooperation Act is signed into law by President Harry S. Truman, authorizing the Marshall Plan.
- April 16, 1948:The Organization for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) is established to administer the Marshall Plan.
- June 30, 1952:The Marshall Plan ends.
Economic Impact: The Marshall Plan Worksheet Answers

The Marshall Plan had a profound economic impact on recipient countries. The massive influx of aid contributed significantly to post-war recovery and reconstruction, helping to rebuild shattered economies and lay the foundation for sustained economic growth.
Industrial Recovery
The Marshall Plan provided crucial support to key industries that had been devastated by the war. The aid funded the reconstruction of factories, mines, and infrastructure, enabling countries to resume production and rebuild their industrial base. Industries such as steel, coal, and transportation benefited significantly from the plan, contributing to increased output and economic recovery.
Infrastructure Development
The Marshall Plan also played a vital role in developing infrastructure, which is essential for economic growth. The aid funded the construction of roads, railways, ports, and power plants, improving transportation, communication, and access to energy. This infrastructure development facilitated trade, investment, and economic activity, contributing to long-term economic prosperity.
Agricultural Modernization
In addition to industrial recovery and infrastructure development, the Marshall Plan also supported agricultural modernization. The aid funded the introduction of new technologies, fertilizers, and improved farming practices, leading to increased agricultural productivity. This resulted in increased food production, reduced dependence on imports, and improved living standards for rural populations.
Political and Social Impact
The Marshall Plan had profound political and social effects on Europe. It contributed to the development of democracy and stability in the region, fostered cooperation and integration among recipient countries, and helped to shape the political landscape of Europe in the post-World War II era.
Influence on Democracy and Stability
The Marshall Plan provided crucial economic support to European countries struggling to rebuild after the war. This aid helped to stabilize economies, reduce poverty, and create jobs, which in turn contributed to the growth of democratic institutions and the consolidation of democracy in Europe.
The plan also helped to strengthen the political center in many countries, reducing the appeal of both communism and extreme nationalism.
Fostering Cooperation and Integration
The Marshall Plan required recipient countries to cooperate with each other in order to receive aid. This cooperation helped to break down barriers between countries that had previously been at war and fostered a sense of common purpose. The plan also encouraged the development of regional organizations, such as the European Coal and Steel Community, which laid the foundation for further European integration.
Shaping the Political Landscape
The Marshall Plan had a significant impact on the political landscape of Europe. It helped to create a more stable and prosperous Europe, which made it less likely that communist or nationalist movements would gain power. The plan also helped to strengthen the transatlantic relationship between the United States and Europe, which became a cornerstone of the Cold War order.
4. Implementation and Challenges

The Marshall Plan’s distribution and management were coordinated by the Economic Cooperation Administration (ECA), established in 1948. The ECA worked closely with European governments to determine aid allocations based on need and the ability to utilize the funds effectively.The plan’s implementation faced numerous challenges.
Political obstacles arose from concerns about Soviet influence in Eastern Europe and the reluctance of some European countries to cooperate with each other. Economic constraints included the need to coordinate currency exchange rates and address inflation caused by the influx of aid.To
overcome these challenges, the ECA engaged in extensive negotiations with European governments, fostering cooperation and consensus. It also established strict accounting and monitoring systems to ensure aid was used effectively and to minimize corruption. Additionally, the ECA provided technical assistance and expertise to help European countries implement economic reforms and boost productivity.
Long-Term Legacy
The Marshall Plan’s long-term impact on Europe and the world was profound. It played a pivotal role in stimulating economic growth, promoting political stability, and fostering international cooperation.
Economic Growth
The Marshall Plan provided Europe with billions of dollars in aid, which helped to rebuild war-torn economies and lay the foundation for sustained economic growth. The plan’s emphasis on infrastructure development, industrial modernization, and trade liberalization contributed to a rapid expansion of European economies.
Political Stability
The Marshall Plan also played a significant role in promoting political stability in Europe. By providing economic assistance to war-torn countries, the plan helped to prevent the spread of communism and the outbreak of further conflict. The plan’s emphasis on democracy and human rights also helped to strengthen democratic institutions in Europe.
International Cooperation
The Marshall Plan was a major catalyst for international cooperation. It brought together the United States, Canada, and Western Europe in a common effort to rebuild Europe. The plan’s success helped to create a sense of unity and cooperation among Western nations that would later form the basis for the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
Comparison to Other Foreign Aid Programs
The Marshall Plan was unique in several ways compared to other foreign aid programs. First, it was much larger in scale than any previous aid program. Second, it was more focused on economic recovery than on humanitarian assistance. Third, it was administered through a multilateral organization, the Organization for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC), which gave European countries a voice in the allocation of aid.
FAQ Compilation
What were the primary goals of the Marshall Plan?
The Marshall Plan aimed to revitalize war-torn Europe, promote economic recovery, and prevent the spread of communism.
Which countries benefited from Marshall Plan aid?
Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, and the United Kingdom received Marshall Plan assistance.
How did the Marshall Plan contribute to economic recovery?
The Marshall Plan provided financial aid, machinery, and technical assistance, which helped rebuild industries, modernize infrastructure, and stimulate economic growth.