Embark on an illuminating journey with the POGIL Ish Light Waves Answer Key, your ultimate companion in unraveling the mysteries of light’s behavior. This meticulously crafted guide provides a comprehensive exploration of the characteristics, interactions, and applications of light waves, empowering you with a profound understanding of this fundamental aspect of our universe.
Delving into the electromagnetic spectrum, we uncover the unique place occupied by light waves. Their properties of wavelength, frequency, and amplitude are examined in detail, revealing the intricate nature of light’s propagation. Furthermore, the enigmatic concept of wave-particle duality is explored, highlighting the paradoxical yet fascinating nature of light.
Light Waves: Characteristics and Behavior
Light waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that fall within a specific range of the electromagnetic spectrum. They exhibit wave-particle duality, meaning they possess both wave-like and particle-like properties. The key characteristics of light waves include wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
Properties of Light Waves, Pogil ish light waves answer key
- Wavelength:The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave.
- Frequency:The number of crests or troughs that pass a given point in one second.
- Amplitude:The maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position.
Wave-Particle Duality
Light waves exhibit wave-particle duality, which means they behave both as waves and particles. This is evident in phenomena such as diffraction and interference, which are wave-like properties, and the photoelectric effect, which is a particle-like property.
Reflection and Refraction of Light
When light waves encounter a boundary between two different media, they can undergo reflection and refraction. Reflection is the bouncing back of light waves from a surface, while refraction is the bending of light waves as they pass from one medium to another.
Law of Reflection
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence (the angle at which light strikes a surface) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which light bounces off the surface).
Refraction
Refraction occurs when light waves pass from one medium to another with different refractive indices. The refractive index is a measure of how much light is bent when it enters a medium. The greater the refractive index, the more the light is bent.
Diffraction and Interference of Light: Pogil Ish Light Waves Answer Key
Diffraction is the spreading out of light waves as they pass through an aperture or around an obstacle. Interference is the superposition of two or more light waves, which can result in constructive or destructive interference.
Diffraction
Diffraction occurs when light waves pass through a narrow opening or around an obstacle. This causes the light waves to spread out and create a diffraction pattern.
Interference
Interference occurs when two or more light waves combine. Constructive interference occurs when the crests of the waves coincide, resulting in a brighter spot. Destructive interference occurs when the troughs of the waves coincide, resulting in a darker spot.
Polarization of Light
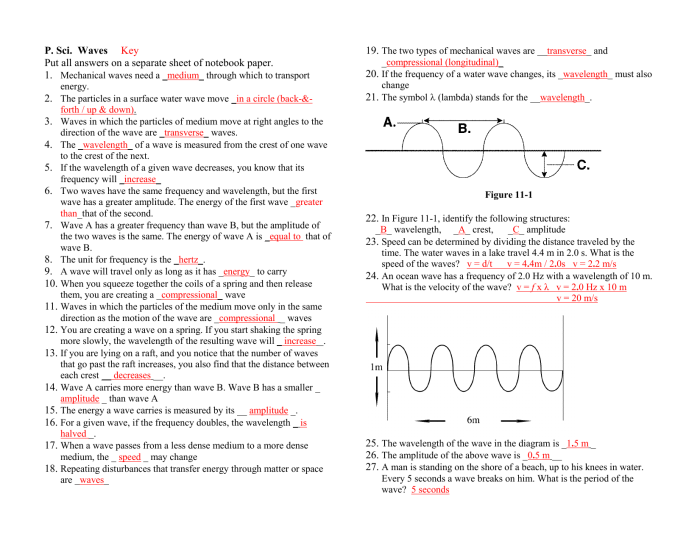
Polarization is a property of light waves that describes the orientation of their electric field. Light waves can be polarized in different ways, including linear, circular, and elliptical polarization.
Types of Polarized Light
- Linearly polarized light:The electric field oscillates in a single direction.
- Circularly polarized light:The electric field rotates in a circle.
- Elliptically polarized light:The electric field rotates in an ellipse.
Applications of Light Waves in Technology
Light waves have a wide range of applications in technology, including communication, medical imaging, and renewable energy.
Communication
- Fiber optics:Light waves are used to transmit data over long distances through optical fibers.
- Lasers:Lasers emit highly concentrated beams of light that are used in various applications, such as telecommunications, optical storage, and laser surgery.
Medical Imaging
- X-rays:X-rays are high-energy light waves that are used to create images of the inside of the body.
- MRI:MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses radio waves and magnetic fields to create detailed images of the inside of the body.
Renewable Energy
- Solar cells:Solar cells convert light energy into electrical energy.
- Photovoltaics:Photovoltaics is the technology of converting light energy into electrical energy using photovoltaic cells.
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of the electromagnetic spectrum in understanding light waves?
The electromagnetic spectrum provides a framework for categorizing light waves based on their energy and wavelength. It helps us understand the relationship between different types of light waves, such as visible light, X-rays, and microwaves.
How does the concept of wave-particle duality apply to light waves?
Wave-particle duality describes the paradoxical nature of light waves, which exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This concept challenges classical physics and has profound implications for our understanding of light’s behavior.
What are the practical applications of reflection and refraction of light?
Reflection and refraction are fundamental principles used in a wide range of optical devices, such as mirrors, lenses, and prisms. They enable us to manipulate light’s path and create various optical effects.

