Embark on a comprehensive exploration of the fundamental principles of macroeconomics with our AP Macroeconomics Unit 3 Practice Test. Dive into the intricacies of fiscal and monetary policies, unravel the factors driving economic growth and inflation, and delve into the complexities of international trade and finance.
This meticulously crafted practice test is designed to equip you with a deep understanding of the key concepts covered in Unit 3. Engage with thought-provoking questions, unravel the rationale behind correct answers, and gain invaluable insights into common misconceptions and pitfalls.
1. Key Concepts and Principles
Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. It is based on the core principles of scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost.
Macroeconomic indicators are important for understanding the health of the economy. Some key indicators include GDP, unemployment rate, and inflation rate.
Macroeconomics and microeconomics are two complementary branches of economics. Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual entities, such as households and firms, while macroeconomics focuses on the economy as a whole.
2. Fiscal Policy

Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. It can be used to stabilize the economy during periods of recession or inflation.
Government spending can stimulate the economy by increasing aggregate demand. Taxation can cool the economy by reducing aggregate demand.
Fiscal policy can have a significant impact on economic growth and inflation. For example, expansionary fiscal policy can lead to higher economic growth but also higher inflation.
3. Monetary Policy
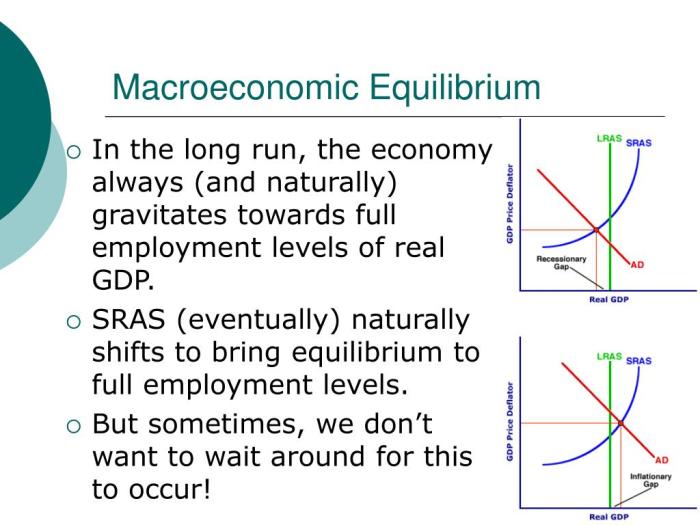
Monetary policy is the use of interest rates to influence the economy. It is conducted by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve.
Central banks can use open market operations, changes in the discount rate, and changes in reserve requirements to influence interest rates.
Monetary policy can have a significant impact on economic growth and inflation. For example, expansionary monetary policy can lead to higher economic growth but also higher inflation.
4. Economic Growth and Inflation
Economic growth is the increase in the value of goods and services produced by an economy over time. It is usually measured by the growth rate of real GDP.
Inflation is the increase in the general price level of goods and services. It is usually measured by the CPI or PPI.
There is a trade-off between economic growth and inflation. Policies that promote economic growth can also lead to higher inflation, and vice versa.
5. International Trade and Finance: Ap Macroeconomics Unit 3 Practice Test
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between countries. It can benefit countries by allowing them to specialize in the production of goods and services that they have a comparative advantage in.
Exchange rates are the prices of one currency in terms of another. They are determined by the forces of supply and demand.
International trade and finance can have a significant impact on the domestic economy. For example, an increase in exports can lead to higher economic growth.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy is employed by governments to influence economic activity through adjustments in government spending and taxation, aiming to stabilize the economy and achieve desired economic outcomes.
How does monetary policy affect economic growth?
Monetary policy, implemented by central banks, influences economic growth by regulating interest rates and managing the money supply. Lower interest rates can stimulate economic activity, while higher interest rates can curb inflation.
What are the potential benefits of international trade?
International trade can foster economic growth, enhance competition, and provide access to a wider range of goods and services. It can also lead to specialization and efficiency gains.