Arrangement of electrons in atoms answer key: Delve into the fascinating world of atomic structure, where electrons dance around the nucleus in a harmonious ballet. This guide unveils the secrets of electron arrangement, empowering you with a profound understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter.
As we embark on this scientific odyssey, we will explore the periodic trends that govern electron configurations, unravel the significance of valence electrons in chemical bonding, and delve into the enigmatic realm of excited states and quantum numbers. Prepare to be captivated as we unlock the mysteries of the atomic realm.
Atomic Structure
An atom is the fundamental building block of matter. It consists of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and electrons, which orbit the nucleus. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element’s atomic number, which uniquely identifies the element.
The electrons in an atom are arranged in energy levels, or shells. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons, and the electrons in each shell have a specific energy.

Electron Arrangement
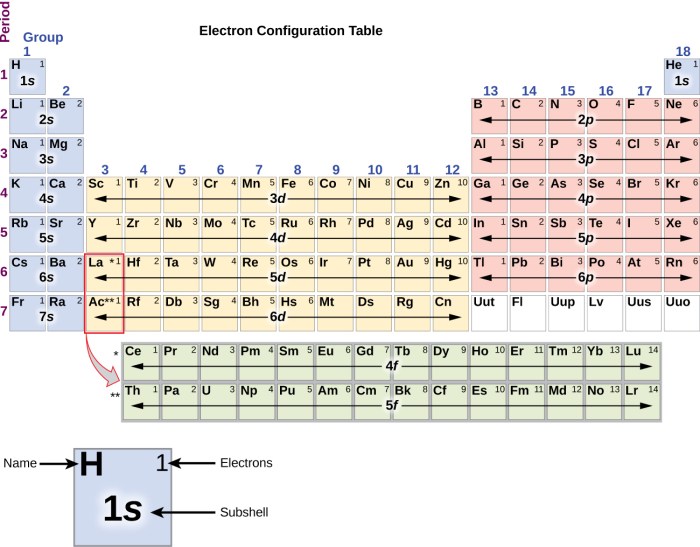
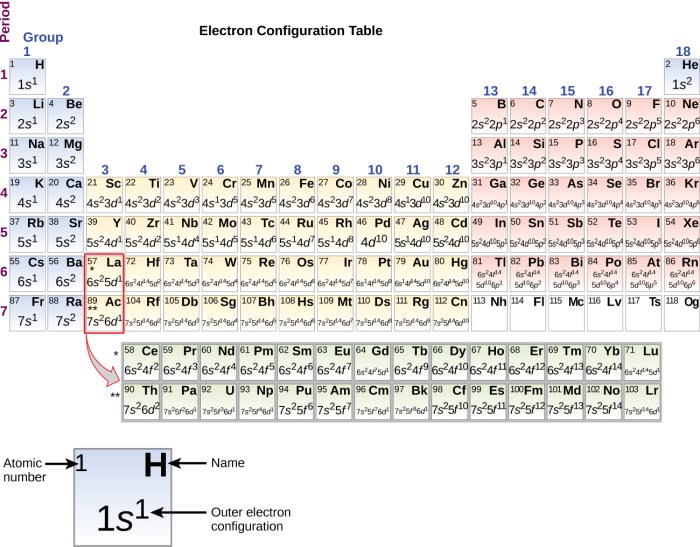
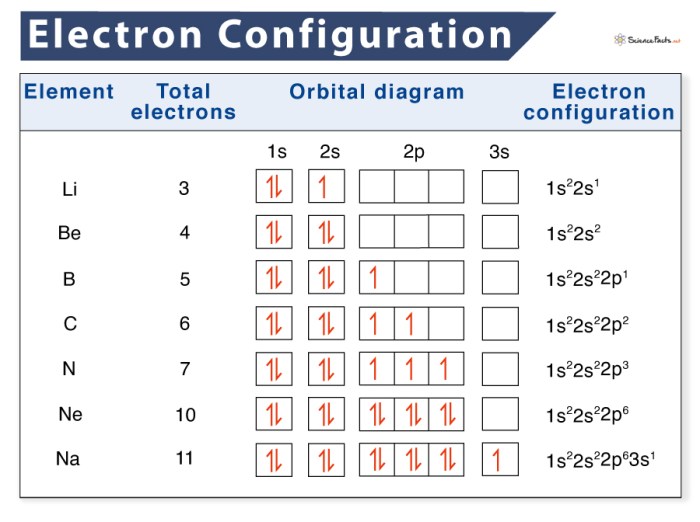
The arrangement of electrons in atoms is determined by the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. The electrons in each shell are further arranged into subshells, which are designated by the letters s, p, d, and f.
Each subshell can hold a specific number of electrons, and the electrons in each subshell have a specific energy.
The electron configuration of an element is the arrangement of electrons in its atoms. The electron configuration can be used to predict the element’s chemical properties.
Periodic Trends, Arrangement of electrons in atoms answer key
The electron configuration of an element affects its chemical properties. For example, elements with similar electron configurations tend to have similar chemical properties. This is because the electron configuration determines the element’s reactivity, ionization energy, and other properties.
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The periodic table can be used to identify trends in electron configuration and chemical properties.
Electron Configurations of Elements
The electron configuration of an element can be determined based on its atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus, and it also equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom of that element.
The electron configuration of an element can be written using the following notation:
1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 3
In this notation, the numbers represent the energy levels, the letters represent the subshells, and the superscripts represent the number of electrons in each subshell.
Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. Valence electrons are involved in chemical bonding, and they determine the element’s chemical properties.
The number of valence electrons an element has can be determined by looking at its electron configuration. The number of valence electrons is equal to the number of electrons in the outermost energy level.
Excited States
An excited state is a state in which an atom has more energy than it does in its ground state. Excited states are created when an electron absorbs energy, which causes it to move to a higher energy level.
Excited states are unstable, and the electrons in an excited state will eventually return to the ground state. When an electron returns to the ground state, it releases energy in the form of a photon.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are numbers that describe the properties of electrons. The four quantum numbers are the principal quantum number (n), the azimuthal quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml), and the spin quantum number (ms).
The principal quantum number (n) describes the energy level of an electron. The azimuthal quantum number (l) describes the shape of the electron’s orbital. The magnetic quantum number (ml) describes the orientation of the electron’s orbital in space. The spin quantum number (ms) describes the spin of the electron.
Quick FAQs: Arrangement Of Electrons In Atoms Answer Key
What is the Aufbau principle?
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting with the lowest energy orbital and progressing to higher energy orbitals as more electrons are added.
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are responsible for chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of an element.
What are quantum numbers?
Quantum numbers are a set of four numbers that describe the properties of an electron. They include the principal quantum number (n), the azimuthal quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml), and the spin quantum number (ms).