Dilations on the coordinate plane answer key – Welcome to the definitive resource on dilations on the coordinate plane! This comprehensive guide, complete with an answer key, will empower you with a thorough understanding of this fundamental geometric transformation. Brace yourself for an enlightening journey as we delve into the fascinating world of dilations.
In this guide, we will explore the intricacies of dilation transformations, uncovering their properties, applications, and matrix representation. Along the way, we will unravel the significance of the center of dilation and witness the remarkable effects of composing dilations. Get ready to expand your geometric horizons and master the art of dilations on the coordinate plane!
Definition of Dilations
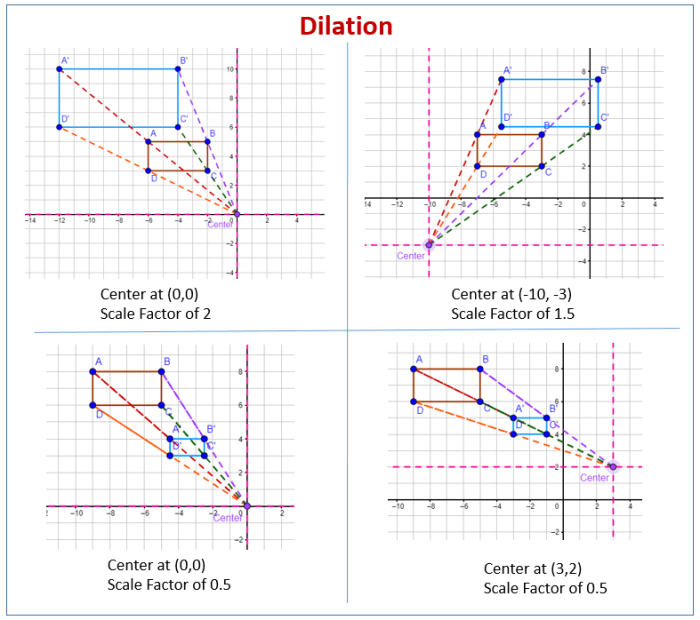
Dilations are transformations that enlarge or shrink a figure on the coordinate plane. They are defined by a scale factor, which determines the amount of enlargement or shrinkage. A scale factor greater than 1 will enlarge the figure, while a scale factor less than 1 will shrink it.
For example, consider a figure with coordinates (1, 2) and (3, 4). If we apply a dilation with a scale factor of 2, the new coordinates will be (2, 4) and (6, 8). This means that the figure has been enlarged by a factor of 2 in both the x and y directions.
Properties of Dilations
Dilations have several important properties:
- They preserve shape: Dilations do not change the shape of a figure. The new figure will be similar to the original figure, but it will be larger or smaller.
- They preserve orientation: Dilations do not change the orientation of a figure. The new figure will be facing the same direction as the original figure.
- The scale factor affects the size and direction of the dilation: The scale factor determines the amount of enlargement or shrinkage. A scale factor greater than 1 will enlarge the figure, while a scale factor less than 1 will shrink it.
The scale factor also determines the direction of the dilation. A scale factor greater than 1 will move the figure away from the center of dilation, while a scale factor less than 1 will move the figure towards the center of dilation.
Center of Dilation
The center of dilation is the point about which a figure is dilated. It is the fixed point that does not move during the dilation. The center of dilation is often denoted by the letter O.
To find the center of dilation, we can use the following formula:
$$O = (\fracx_1 + x_22, \fracy_1 + y_22)$$
where $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$ are the coordinates of any two points on the figure.
Matrix Representation of Dilations
Dilations can be represented by matrices. The matrix for a dilation with a scale factor of k is:
$$\beginbmatrix k & 0 \\\ 0 & k \endbmatrix$$
To perform a dilation using a matrix, we simply multiply the matrix by the coordinates of the points in the figure. For example, to perform a dilation with a scale factor of 2 about the origin, we would use the following matrix:
$$\beginbmatrix 2 & 0 \\\ 0 & 2 \endbmatrix$$
And we would multiply this matrix by the coordinates of each point in the figure.
Composition of Dilations: Dilations On The Coordinate Plane Answer Key
Dilations can be composed to create more complex transformations. When two dilations are composed, the resulting transformation is a dilation with a scale factor that is the product of the scale factors of the individual dilations.
For example, if we compose a dilation with a scale factor of 2 about the origin with a dilation with a scale factor of 3 about the origin, the resulting transformation will be a dilation with a scale factor of 6 about the origin.
Applications of Dilations
Dilations have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Graphics: Dilations are used to scale and resize images.
- Engineering: Dilations are used to enlarge or shrink objects in design and manufacturing.
- Design: Dilations are used to create patterns and textures.
FAQ Explained
What is a dilation transformation?
A dilation transformation is a geometric transformation that enlarges or reduces a figure by a specific factor, known as the scale factor.
How do you find the center of dilation?
The center of dilation is the fixed point around which the figure is enlarged or reduced. To find the center of dilation, you can use the midpoint formula or the intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the line segments connecting corresponding points on the original and dilated figures.
What is the matrix representation of a dilation transformation?
The matrix representation of a dilation transformation is a 2×2 matrix that scales the figure by the specified scale factor. The matrix is given by [k 0; 0 k], where k is the scale factor.