A hydronic system provides comfort heating by producing radiant heat, offering a gentle and enveloping warmth that is evenly distributed throughout a space. Unlike forced-air systems that can create drafts and uneven temperatures, hydronic heating delivers a consistent and comfortable environment.
This innovative heating method utilizes water as a heat transfer medium, circulating it through a network of pipes embedded within the floor, walls, or ceiling. As the water flows through these pipes, it releases heat into the surrounding air, creating a cozy and inviting atmosphere.
System Overview

A hydronic heating system provides comfort heating by producing warm water and distributing it throughout a building. It operates on the principle of heat transfer through a circulating fluid, typically water or a water-based solution.
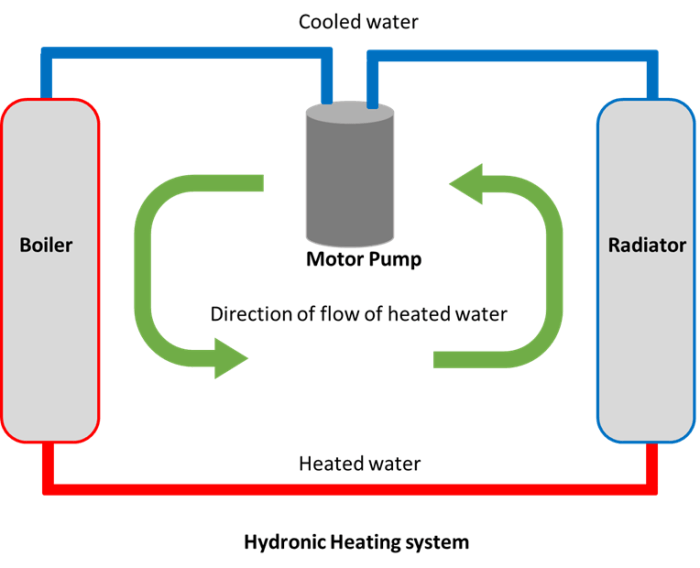
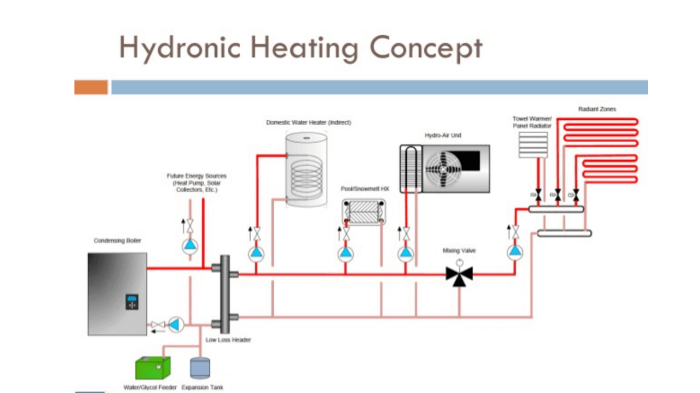
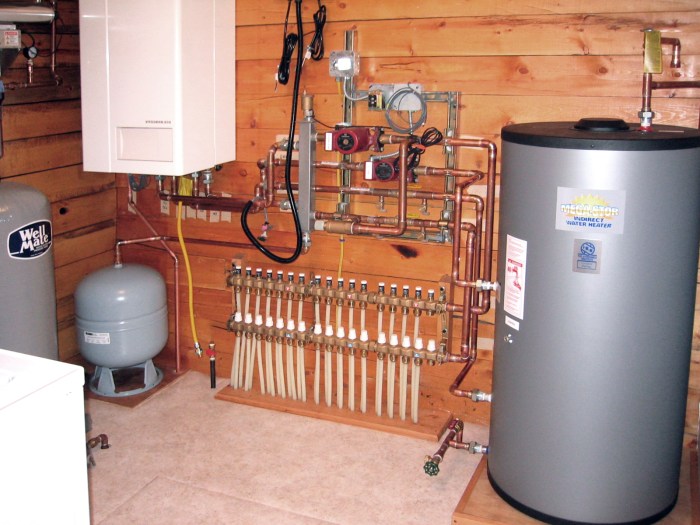
The system comprises several components, including a heat source (boiler), a pump to circulate the fluid, piping and tubing to distribute the warm water, and heat emitters (radiators, convectors, or underfloor heating) to release heat into the space.
Comfort Heating
Hydronic systems provide comfort heating by distributing radiant heat through the heat emitters. Radiant heat warms objects and surfaces directly, creating a comfortable and evenly distributed warmth throughout the space.
Unlike forced-air systems that circulate warm air, hydronic systems do not cause air movement, resulting in reduced dust and allergen circulation. Additionally, they provide better temperature control and zoning options, allowing for tailored comfort levels in different areas of the building.
Heat Production, A hydronic system provides comfort heating by producing
Heat in a hydronic system is typically generated by a boiler, which can be fueled by natural gas, oil, electricity, or renewable sources such as solar or geothermal energy.
Gas and oil boilers are common options, offering high efficiency and reliability. Electric boilers are an alternative for buildings without access to gas or oil, while solar and geothermal boilers provide sustainable heating solutions.
Distribution and Control
The hydronic piping system is designed to distribute warm water from the heat source to the heat emitters. Piping materials include copper, PEX tubing, and steel.
Pumps circulate the water through the system, and valves control the flow and temperature of the water to individual heat emitters. Temperature regulation is achieved through thermostats or zone controllers, allowing for precise temperature control in different areas of the building.
Efficiency and Sustainability
Hydronic heating systems are highly energy efficient due to their ability to transfer heat effectively and distribute it evenly throughout the space. They can operate at lower water temperatures than forced-air systems, reducing energy consumption.
By using renewable energy sources such as solar or geothermal energy, hydronic systems can significantly reduce fossil fuel consumption and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of a hydronic heating system. This includes annual inspections, cleaning of components, and water treatment to prevent corrosion and scale buildup.
Common troubleshooting issues include leaks, air in the system, and pump failures. Regular maintenance can help identify and resolve potential problems before they become major issues.
Quick FAQs: A Hydronic System Provides Comfort Heating By Producing
What are the benefits of a hydronic heating system?
Hydronic heating systems offer several benefits, including:
- Even and consistent heat distribution
- Improved energy efficiency
- Reduced noise levels
- Enhanced indoor air quality
How does a hydronic heating system work?
A hydronic heating system circulates heated water through a network of pipes embedded in the floor, walls, or ceiling. As the water flows through the pipes, it releases heat into the surrounding air, warming the space.
Is a hydronic heating system more efficient than a forced-air system?
Yes, hydronic heating systems are generally more efficient than forced-air systems. This is because water has a higher heat capacity than air, meaning it can store more heat and release it more evenly over time.