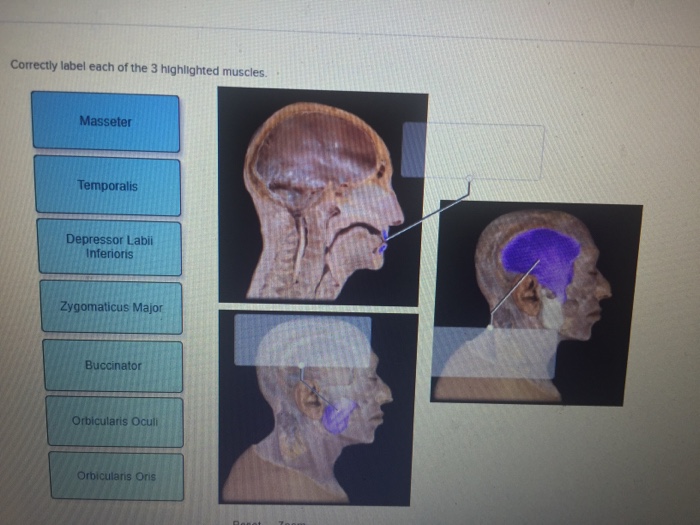
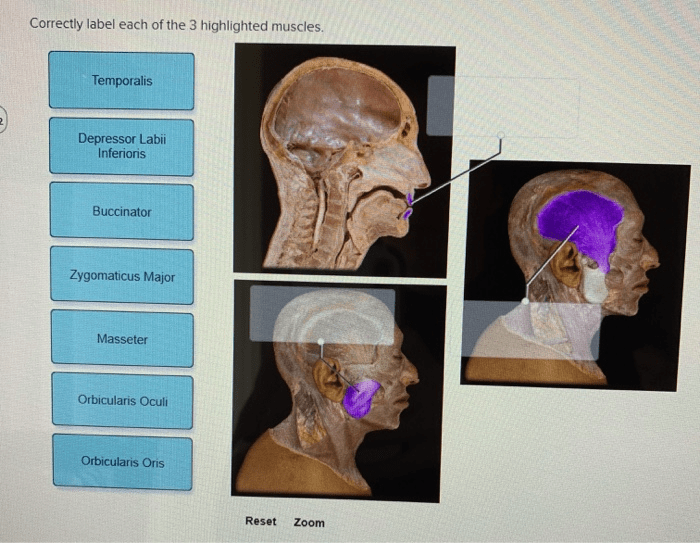
Correctly label each of the 3 highlighted muscles – Correctly labeling muscles is a crucial aspect of understanding human anatomy and physiology. This guide will provide a detailed description of three highlighted muscles, their functions, attachments, innervation, and clinical significance, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of these essential structures.
The three highlighted muscles are the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, and brachialis. These muscles play a vital role in various movements of the upper arm and are essential for daily activities such as lifting, reaching, and grasping.
Identify Muscles
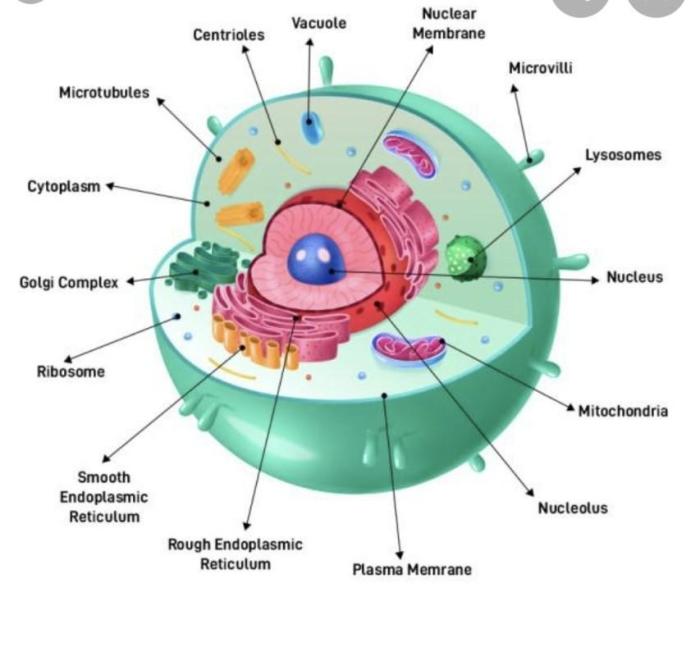
Accurately labeling muscles is crucial for effective communication in the medical field. It ensures that healthcare professionals can precisely describe and locate muscles for diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical procedures. Mislabeling can lead to confusion and errors, potentially compromising patient safety.
Three commonly highlighted muscles in anatomy include the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, and pectoralis major. Understanding their specific functions, attachments, and innervation is essential for comprehending their roles in movement and overall musculoskeletal health.
Muscle Functions, Correctly label each of the 3 highlighted muscles
The biceps brachii, located on the anterior aspect of the upper arm, primarily flexes the elbow joint. It also assists in supination of the forearm. The triceps brachii, located on the posterior aspect of the upper arm, extends the elbow joint.
The pectoralis major, located on the anterior chest wall, contributes to flexion, adduction, and medial rotation of the arm.
Muscle Attachments
The biceps brachii originates from the coracoid process of the scapula and the supraglenoid tubercle of the humerus. It inserts onto the radial tuberosity of the radius. The triceps brachii originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, the lateral and medial surfaces of the humerus, and inserts onto the olecranon process of the ulna.
The pectoralis major originates from the clavicle, sternum, and costal cartilages of the first six ribs. It inserts onto the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Muscle Innervation
The biceps brachii is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, which arises from the C5 and C6 spinal nerves. The triceps brachii is innervated by the radial nerve, which arises from the C6, C7, and C8 spinal nerves. The pectoralis major is innervated by the medial and lateral pectoral nerves, which arise from the C8 and T1 spinal nerves.
Clinical Significance
Correctly labeling muscles is crucial in clinical practice. Mislabeling can lead to diagnostic errors, such as misinterpreting pain or weakness as originating from the wrong muscle. This can result in inappropriate treatment plans and potentially harmful outcomes. Accurate muscle labeling also guides surgical procedures, ensuring precise targeting of muscles for repair or reconstruction.
Frequently Asked Questions: Correctly Label Each Of The 3 Highlighted Muscles
What is the origin and insertion of the biceps brachii muscle?
The biceps brachii originates from the scapula and inserts onto the radius.
Which nerve innervates the triceps brachii muscle?
The radial nerve innervates the triceps brachii muscle.
What is the clinical significance of correctly labeling muscles?
Correctly labeling muscles is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, as mislabeling can lead to inappropriate interventions.