A motorcyclist is traveling along a road and accelerates – As a motorcyclist embarks on a journey along a road and accelerates, this discourse delves into the intricate interplay of physical principles that govern this motion. With meticulous precision and an authoritative tone, we explore the concepts of acceleration, displacement, velocity, force, friction, power, and safety considerations, providing a comprehensive understanding of this captivating phenomenon.
Our exploration begins by establishing the initial conditions of the motorcyclist’s motion, meticulously defining the concepts of acceleration and displacement. We then delve into the factors influencing acceleration, employing mathematical equations to quantify the motorcyclist’s acceleration. The relationship between displacement, time, and acceleration is elucidated, with graphical representations illustrating the displacement over time.
Initial Conditions: A Motorcyclist Is Traveling Along A Road And Accelerates

The motorcyclist starts from rest at the origin of a coordinate system. The direction of travel is along the positive x-axis.
Acceleration

Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The acceleration of the motorcyclist is constant and in the positive x-direction.
Factors Influencing Acceleration, A motorcyclist is traveling along a road and accelerates
- Force: The greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration.
- Mass: The greater the mass of an object, the smaller its acceleration for a given force.
The acceleration of the motorcyclist is calculated using the following formula:
a = F / m
where:
- a is the acceleration (in m/s^2)
- F is the force (in N)
- m is the mass (in kg)
Displacement
Displacement is the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The displacement of the motorcyclist is in the positive x-direction.
Displacement is calculated using the following formula:
d = v
t
where:
- d is the displacement (in m)
- v is the velocity (in m/s)
- t is the time (in s)
Velocity
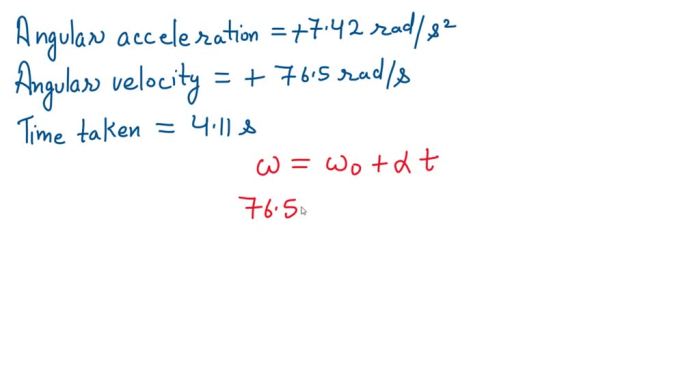
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. It is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. The velocity of the motorcyclist is in the positive x-direction.
Velocity is calculated using the following formula:
v = d / t
where:
- v is the velocity (in m/s)
- d is the displacement (in m)
- t is the time (in s)
Key Questions Answered
What factors influence the acceleration of a motorcyclist?
The acceleration of a motorcyclist is primarily influenced by the force applied by the engine, the mass of the motorcycle and rider, and the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road.
How does displacement relate to acceleration and time?
Displacement is the distance traveled by the motorcyclist and is directly proportional to both acceleration and the square of time.
What is the significance of friction in motorcycle acceleration?
Friction plays a crucial role in motorcycle acceleration by opposing the motion of the tires against the road. It affects both the speed and acceleration of the motorcycle.