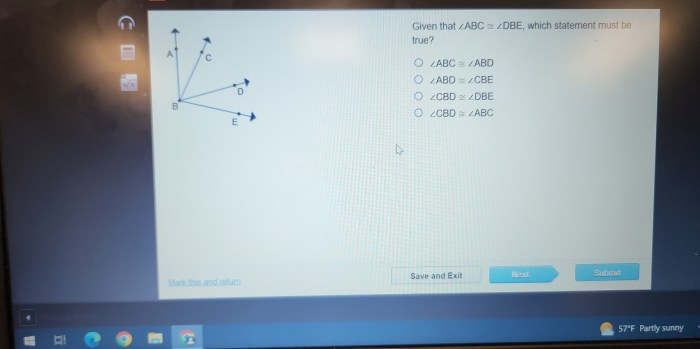
Given that abc dbe which statement must be true – Given that ABC DBE, which statement must be true? This question delves into the realm of logical reasoning and deduction, exploring the intricate relationships between given statements and their implications. By examining the structure and content of given statements, we can derive true statements and make logical inferences, uncovering hidden truths and expanding our understanding of the world around us.
As we embark on this intellectual journey, we will explore the concepts of related statements, true statements, conditional statements, and logical inferences. Through examples and explanations, we will unravel the mechanisms by which given statements shape our understanding of the world and empower us to make informed decisions.
Given and Related Statements
Given statements are those that are assumed to be true or accepted as facts. Related statements are those that are logically connected to given statements and can be inferred from them. The relationship between given and related statements is important because it allows us to make logical inferences and derive new conclusions.
For example, if we are given the statement “All dogs are mammals,” we can infer the related statement “Some mammals are dogs.” This is because the given statement implies that all dogs belong to the class of mammals, and therefore some members of the class of mammals must be dogs.
Implications of Given Statements on Related Statements, Given that abc dbe which statement must be true
The implications of given statements on related statements can be significant. Given statements can limit the scope of possible related statements and can also provide support for or against certain related statements. For example, if we are given the statement “No cats are dogs,” we can infer that it is impossible for a related statement to be true that claims “Some dogs are cats.”
This is because the given statement rules out the possibility of any overlap between the classes of cats and dogs.
True Statements
True statements are those that are consistent with reality and can be verified through observation or logical reasoning. In the context of given statements, true statements are those that are logically derived from the given statements and are not contradicted by any other known facts.
The criteria for determining if a statement is true include:
- Consistency with given statements:The statement must not contradict any of the given statements.
- Logical coherence:The statement must be logically consistent with itself and with other known facts.
- Empirical verification:The statement can be verified through observation or experimentation.
How to Derive True Statements from Given Statements
True statements can be derived from given statements using a variety of logical reasoning techniques, including:
- Deduction:Deduction is a logical process that allows us to derive new statements from given statements that are logically implied by them.
- Induction:Induction is a logical process that allows us to make general statements based on the observation of specific instances.
Conditional Statements
Conditional statements are statements that express a relationship between two or more events or conditions. They have the form “if p, then q,” where p is the antecedent (the condition) and q is the consequent (the result).
Conditional statements can be used to represent given statements and to derive new conclusions. For example, if we are given the conditional statement “If it is raining, then the ground is wet,” we can infer the related statement “If the ground is wet, then it is raining.”
This is because the conditional statement implies that the antecedent (raining) is a sufficient condition for the consequent (ground being wet).
Relationship between Given Statements and Conditional Statements
Given statements can be used to construct conditional statements. For example, if we are given the statement “All dogs are mammals,” we can construct the conditional statement “If something is a dog, then it is a mammal.” This conditional statement captures the logical relationship between the given statement and the related statement “Some mammals are dogs.”
Logical Inferences
Logical inferences are conclusions that are derived from given statements using logical reasoning. They are based on the assumption that the given statements are true and that the logical rules of inference are valid.
The process of making logical inferences involves:
- Identifying the given statements:The first step is to identify the given statements that are relevant to the inference.
- Applying logical rules:The next step is to apply logical rules of inference to the given statements to derive new conclusions.
- Evaluating the conclusions:The final step is to evaluate the conclusions to ensure that they are consistent with the given statements and with other known facts.
Role of Deduction and Induction in Logical Inferences
Deduction and induction are two important logical reasoning techniques that are used to make logical inferences. Deduction is a top-down approach that allows us to derive new statements from given statements that are logically implied by them. Induction is a bottom-up approach that allows us to make general statements based on the observation of specific instances.
Table of Examples
| Given Statement | Related Statement | True Statement | Logical Inference |
|---|---|---|---|
| All dogs are mammals. | Some mammals are dogs. | Dogs are vertebrates. | If something is a dog, then it is a mammal. |
| No cats are dogs. | Some dogs are not cats. | Cats and dogs are different species. | If something is a cat, then it is not a dog. |
| If it is raining, then the ground is wet. | If the ground is wet, then it is raining. | Rain is a necessary condition for the ground to be wet. | If the ground is not wet, then it is not raining. |
Frequently Asked Questions: Given That Abc Dbe Which Statement Must Be True
What is the difference between a given statement and a related statement?
A given statement is a statement that is presented as true without providing any justification or evidence. A related statement is a statement that is derived from a given statement through logical reasoning or deduction.
How can we determine if a statement is true?
A statement is true if it is consistent with all known facts and logical principles. We can determine if a statement is true by examining its logical structure, considering its implications, and comparing it to other known facts.
What is the purpose of a conditional statement?
A conditional statement is a statement that expresses a relationship between two or more statements. The purpose of a conditional statement is to specify the conditions under which a particular statement is true.