Chapter 9 Test B Geometry Answers: Unleash your inner geometry ninja and conquer the test with confidence! Get ready to delve into a world of shapes, angles, and problem-solving techniques.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies you need to tackle every question on the test head-on. From multiple-choice questions to mind-boggling problem-solving challenges, we’ve got you covered.
Geometry Chapter 9 Test B Overview: Chapter 9 Test B Geometry Answers
Geometry Chapter 9 Test B assesses students’ understanding of various geometry concepts, including transformations, similarity, and congruence.
The test covers the following key topics:
Transformations
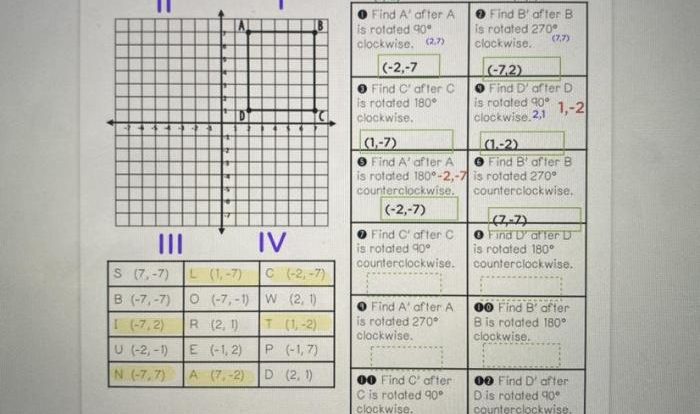
- Identifying and applying transformations (translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations)
- Understanding the effects of transformations on shapes and their properties
Similarity
- Determining if two figures are similar
- Using similarity transformations to solve problems
- Applying the concept of scale factor in similar figures
Congruence
- Recognizing and proving congruent figures
- Applying congruence criteria (SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS)
- Solving problems involving congruent triangles and other shapes
Types of Questions
Geometry Chapter 9 Test B comprises diverse question types, each requiring specific skills and knowledge.
The test includes:
- Multiple Choice:These questions present several options, requiring you to select the correct answer. They test your understanding of concepts and vocabulary.
- Short Answer:These questions require you to provide brief, concise answers, typically involving definitions, formulas, or explanations. They assess your ability to recall and apply knowledge.
- Problem-Solving:These questions present complex scenarios that require you to demonstrate your problem-solving skills. They involve applying concepts and formulas to solve real-world problems.
Study Strategies
Effective preparation for the Geometry Chapter 9 Test B is crucial for success. This section provides valuable study strategies to help you excel in the test. By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your understanding of key concepts, prioritize essential topics, and allocate your time wisely.
One effective strategy is to create a study schedule that accommodates your learning style and availability. Prioritize key concepts and allocate more time to areas where you need additional support. Utilizing textbooks, online resources, and practice problems can reinforce your understanding and identify areas for improvement.
Recommended Resources
- Geometry textbook
- Online practice problems: Khan Academy, Mathway
- Supplemental study materials: notes, flashcards
Time Management
Time management is essential for success in any exam. Allocate your study time wisely, focusing on key concepts and areas where you need improvement. Break down the material into smaller chunks to avoid feeling overwhelmed and to enhance comprehension.
Prioritizing Key Concepts
Identify the most important concepts covered in Chapter 9 and focus your efforts on mastering them. These key concepts often form the foundation for more complex topics and are frequently tested on exams. By prioritizing these concepts, you can maximize your chances of success.
Common Errors and Misconceptions
Students often make certain errors or hold misconceptions while taking the Geometry Chapter 9 Test B. These can stem from a lack of understanding of concepts, misinterpretation of questions, or careless mistakes.One common error is confusing the definitions of similar geometric shapes.
For example, students may mistake a parallelogram for a rectangle or a trapezoid for a quadrilateral. It is crucial to carefully review the definitions and characteristics of different shapes to avoid such errors.Another common misconception is assuming that all angles in a triangle add up to 90 degrees.
While this is true for right triangles, it is not the case for all triangles. The sum of interior angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees.Careless mistakes, such as misreading numbers or forgetting to label answers, can also lead to errors.
To avoid these, students should carefully read the questions, check their work, and ensure they have labeled their answers correctly.By understanding these common errors and misconceptions and employing strategies to avoid them, students can improve their performance on the Geometry Chapter 9 Test B.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practice problems are an essential part of preparing for the Geometry Chapter 9 Test B. They provide an opportunity to test your understanding of the concepts and to identify areas where you need additional practice.The table below provides a list of practice problems that are relevant to the test topics.
The solutions to the problems are provided in the following paragraphs.
Types of Quadrilaterals
- Classify the quadrilateral with vertices (2, 3), (6, 3), (8, 7), and (4, 7).
- Find the area of a parallelogram with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm.
Properties of Parallelograms
- Prove that the opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent.
- Find the measure of an angle in a parallelogram if one of the adjacent angles measures 120 degrees.
Properties of Trapezoids
- Find the area of a trapezoid with bases of 10 cm and 15 cm and a height of 8 cm.
- Prove that the diagonals of a trapezoid bisect each other.
Properties of Kites
- Find the area of a kite with diagonals of 10 cm and 15 cm.
- Prove that the diagonals of a kite are perpendicular to each other.
Properties of Rhombuses and Squares, Chapter 9 test b geometry answers
- Find the perimeter of a rhombus with a side length of 10 cm.
- Prove that the diagonals of a square bisect each other perpendicularly.
Solutions
1. Classify the quadrilateral with vertices (2, 3), (6, 3), (8, 7), and (4, 7).The quadrilateral is a parallelogram because it has opposite sides that are parallel and congruent. 2. Find the area of a parallelogram with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm.The area of a parallelogram is given by the formula A = bh, where b is the length of the base and h is the height.
In this case, the base is 10 cm and the height is 8 cm, so the area is A = 10 cm
8 cm = 80 cm2.
3. Prove that the opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent.Let ABCD be a parallelogram. Then, ∠A = ∠C and ∠B = ∠D because opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel. 4. Find the measure of an angle in a parallelogram if one of the adjacent angles measures 120 degrees.Since the opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent, if one angle measures 120 degrees, then the other adjacent angle also measures 120 degrees.
5. Find the area of a trapezoid with bases of 10 cm and 15 cm and a height of 8 cm.The area of a trapezoid is given by the formula A = (b 1+ b 2)h/2, where b 1and b 2are the lengths of the bases and h is the height. In this case, the bases are 10 cm and 15 cm and the height is 8 cm, so the area is A = (10 cm + 15 cm)8 cm/2 = 100 cm 2. 6. Prove that the diagonals of a trapezoid bisect each other.Let ABCD be a trapezoid.
Then, the diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at point E. This is because the diagonals of a trapezoid divide the trapezoid into two congruent triangles. 7. Find the area of a kite with diagonals of 10 cm and 15 cm.The area of a kite is given by the formula A = (d 1d 2)/2, where d 1and d 2are the lengths of the diagonals.
In this case, the diagonals are 10 cm and 15 cm, so the area is A = (10 cm
15 cm)/2 = 75 cm2.
8. Prove that the diagonals of a kite are perpendicular to each other.Let ABCD be a kite. Then, the diagonals AC and BD are perpendicular to each other. This is because the diagonals of a kite bisect each other at right angles. 9. Find the perimeter of a rhombus with a side length of 10 cm.The perimeter of a rhombus is given by the formula P = 4s, where s is the length of a side.
In this case, the side length is 10 cm, so the perimeter is P = 4
10 cm = 40 cm.
10. Prove that the diagonals of a square bisect each other perpendicularly.Let ABCD be a square. Then, the diagonals AC and BD bisect each other perpendicularly. This is because the diagonals of a square are perpendicular to each other and bisect each other at the center of the square.
Tips for Success
To excel in the Geometry Chapter 9 Test B, it is crucial to adopt effective study strategies. This involves reviewing notes, practicing regularly, and seeking assistance when necessary. By following these tips, you can enhance your understanding of the concepts and improve your performance on the test.
Review Notes Regularly
- Revisiting your notes regularly helps reinforce the concepts and improves retention.
- Focus on understanding the key ideas and concepts rather than just memorizing facts.
- Summarize the main points and highlight important formulas and theorems.
Practice Regularly
- Regular practice is essential for developing proficiency in solving geometry problems.
- Attempt various types of problems to gain exposure to different scenarios.
- Start with easier problems and gradually progress to more challenging ones.
Seek Help When Needed
- Don’t hesitate to seek assistance if you encounter difficulties understanding a concept or solving a problem.
- Consult with your teacher, a tutor, or a classmate who can provide guidance.
- Utilize online resources such as videos, tutorials, and forums to supplement your learning.
FAQs
Q: What types of questions can I expect on Chapter 9 Test B Geometry?
A: You’ll encounter a mix of multiple-choice, short answer, and problem-solving questions that test your understanding of geometry concepts.
Q: How can I prepare effectively for the test?
A: Review your notes thoroughly, practice solving problems from your textbook and online resources, and don’t hesitate to ask for help from your teacher or a tutor if needed.
Q: What are some common errors to avoid on the test?
A: Make sure to read the questions carefully, avoid careless mistakes, and double-check your answers before submitting the test.